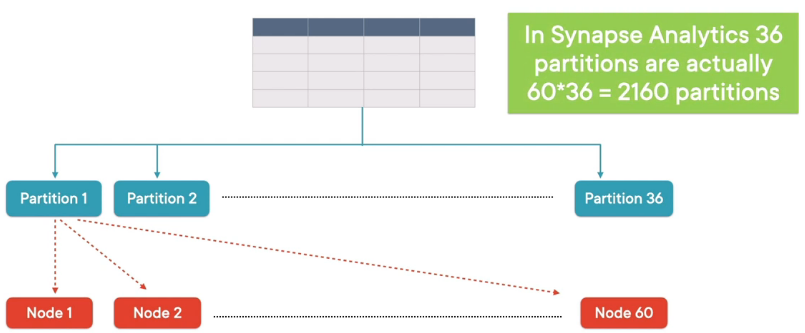
For optimal performance and compressing across Clustered Columnstore Index (CCI), we need to ensure that each partition/ distribution should have at minimum 1 million records
If each partition will have less than 60 million rows then it is recommended to reduce the number of partitions
Partitioning Tables in Dedicated SQL Pool - Azure Synapse Analytics | Microsoft Docs
Types of Distribution
Hash Distribution
Distributes the rows across the compute nodes using a deterministic hash function
Distributes the data evenly so that Synapse compute power can be properly utilized
Works well for tables bigger than 2 GB
Used on tables that frequently receive insert, update and delete operations
Generally used for Fact Tables in Star Schema
Round Robin
It is the default distribution type in Synapse
Assigns rows evenly across the nodes. The data is distributed in the nodes randomly
There is no guarantee that similar data is going to be stored on the same node
Joining a round-robin table will always result in reshuffling resulting in a performance hit
Round Robin can be used if the table has no joining key or joins are performed very infrequently
If no column can distribute the data evenly use hash distribution
Temporary tables are generally created using Round Robin distribution
Replicated
It is a table that gets distributed across all 60 nodes of Synapse
Useful for small tables and tables that are joined frequency against a big fact table
Dimension tables are generally created using replicated distribution
Hash Key Characteristics
The column should be used for grouping operations. The grouped records should lie in 1 distribution
The hash key is used as a join condition, especially for large tables. This will prevent unnecessary data movement
Has more than 60 distinct keys so that the data can be distributed across the 60 nodes in Synapse (Many unique values)
It should not be a date column and should have very few (ideally no) NULL values
Best Practices
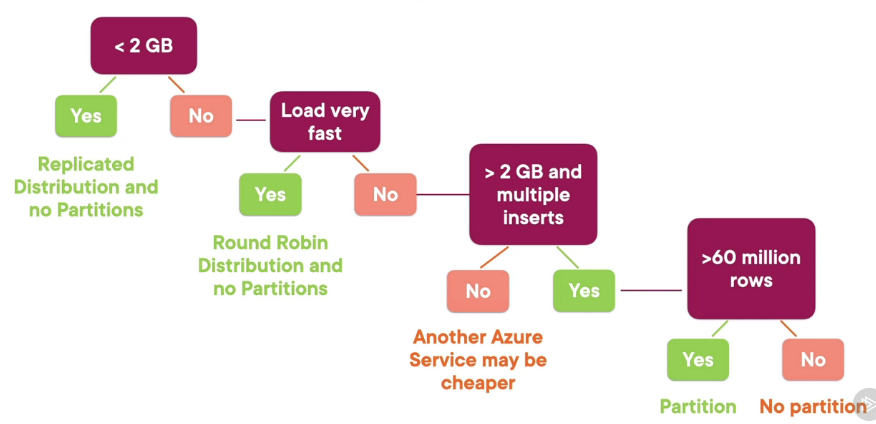
For more than 60 million records Clustered Columnstore Index (CCI) provides the best performance
For smaller tables heap and Clustered Index will provide better performance
Heaps are useful for temporary storage and are a great choice for staging tables
For Hash distribution, the column that is extensively used in join should be used
If round robin is used on a dimension table then the column used in the grouping operation should be used as a key
Round Robin tables provide good speed when performing data load operations
Frequently run queries are cached by Synapse at the Control Node
We should not enable cache when working with large datasets as it will throttle the control nodes and degrade the overall performance
Cheatsheet for Dedicated SQL Pool - Azure Synapse Analytics | Microsoft Learn