Break large physical LAN into smaller logical LANs
This feature can be configured on managed switches
Assigns specific switch interfaces (ports) on the switch to specific VLANs (Port 1, 2, 3 - VLAN 100 and Port 4, 5, 6 - VLAN 200, etc.)
VLANs reduce broadcast domain
Allows to Segments network by role (HR, Sales). Increases security
Devices on one VLAN cannot communicate with devices on another VLAN
VLANs can span multiple physical switches
These VLANs on different switches can be joined together using Ethernet
This solution but it does not scale well when there are multiple VLANs
A lot of ports will be used up just to link the switches together
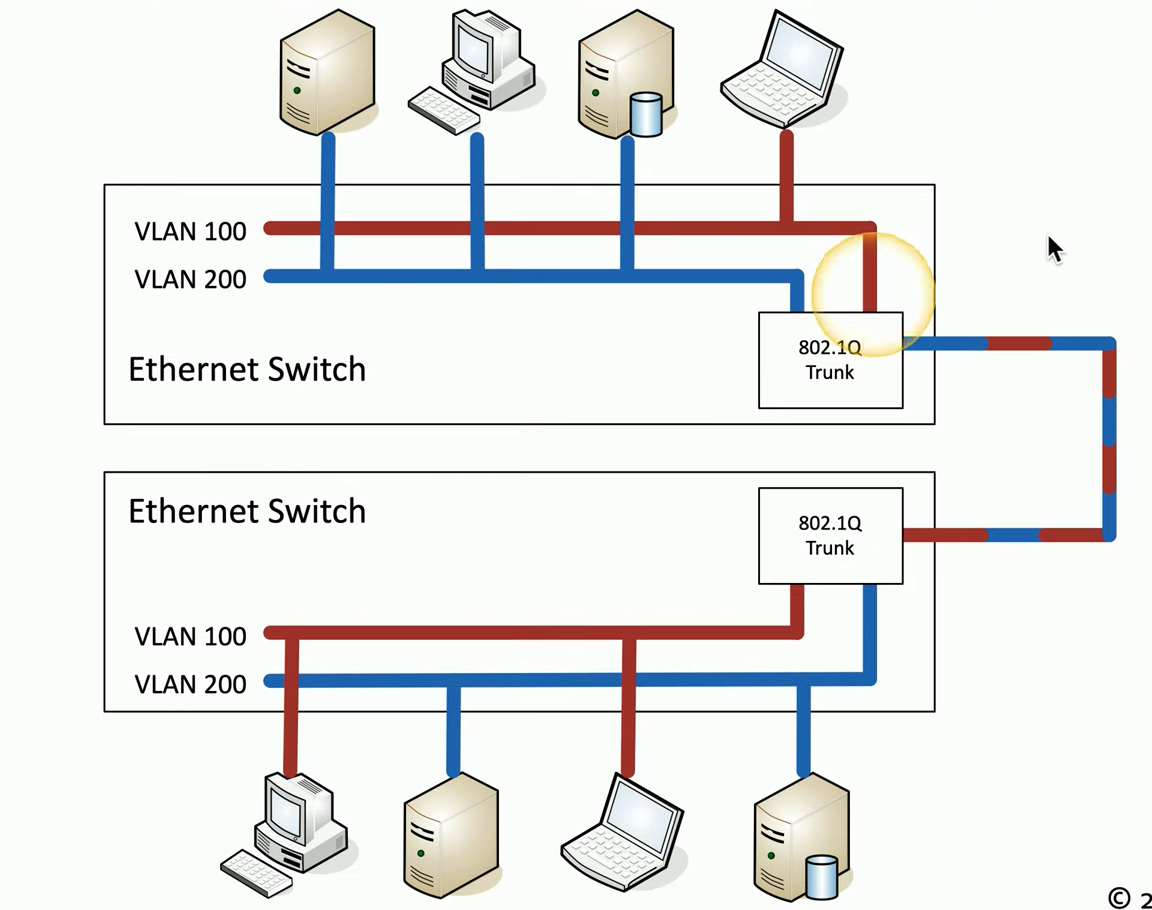
VLAN Trunking
Part of the 802.1q standard
Allows a single interface (port) on the switch to act as a bridge for all the VLANs (Trunk Link)
When packet is sent over the Trunk an additional header called VLAN header is added to each packet
This header has two parts: Tag Protocol Identifier (TPI) & Tag Control Identifier (TCI)
The details in this header allows the packet to find the correct VLAN
The VLAN that is left untagged becomes the default VLAN also called VLAN 0