Converts Private IP Address to Public IP Address
Allows to map multiple private IP Addresses to a single public IP
Types of NAT
Static NAT (SNAT)
Translates private IP Address to a fixed public IP Address
If multiple devices on the network, for each device a public IP Address is required
SNAT does not utilize a NAT table
This type of NAT is used on Web Servers that are exposed publicly where the port is fixed
Static NAT does not converse any IP Addresses
Dynamic NAT (DNAT)
Maps each private IP Address to a different public IP Address (Modifies Layer 3 header)
The private to public address mapping is performed using a Pool of reserved public address
The public IP is selected dynamically from the pool
PAT (Port Address Translation)
It is also a type of DNAT. Most commonly used in home networks
It is also called NAT Overloading, Network & Port Translation (NAPT) & IP Masquerading
Maps multiple private IP Address to a single public IP Address by changing the IP Address & port number (Modify Layer 3 & Layer 4 headers)
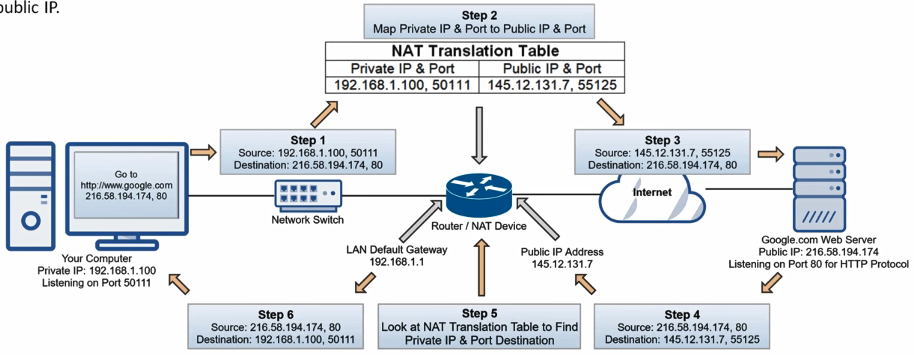
Working
Router has 2 interfaces: Public and Private
Lets assume we want to connect to google.com from our Laptop
Step 1: Generate a request to sent to Google Server which is listening on port 80 from our devices Private IP Address on a Random High Port
Step 2: NAT maps our devices private IP and port to its public IP and random port. This information (mapping) is stored in the NAT translation table. If there is no port conflict then the port number is not changed by NAT
Step 3: Router will forward the packet to google web server which will appear to have originated from the public IP address of our router
Step 4: Google sends back reply on our public IP address
Step 5: NAT looks for the destination IP Address and Port and looks mapping that matches the incoming request
Step 6: The packet is forwarded to the appropriate device on the LAN