Switch has an internal table which is used to stores the mapping between its ports and the MAC Address of the device connected to its port
Working
Host A wants to sends frame (data) to Host B (It does not know its MAC Address)
Host A sends out an ARP packet to its switch asking for the MAC Address of Host B
This data frame consist of the Source and Destination MAC Address
Switch records Host As MAC Address on the port the data entered (Learning)
If switch does not know the MAC Address of Host B it duplicates the ARP packet and floods it on all the ports leaving source port (Flooding)
The devices for which the data was not meant will discard the ARP packet silently
When the ARP packet reaches Host B, it responds back to the switch with its MAC Address
The switch adds Host Bs MAC address to its table and forwards the packet to Host A
Since switch already knows Host As location it forwards the packet only on its port (Forwarding)
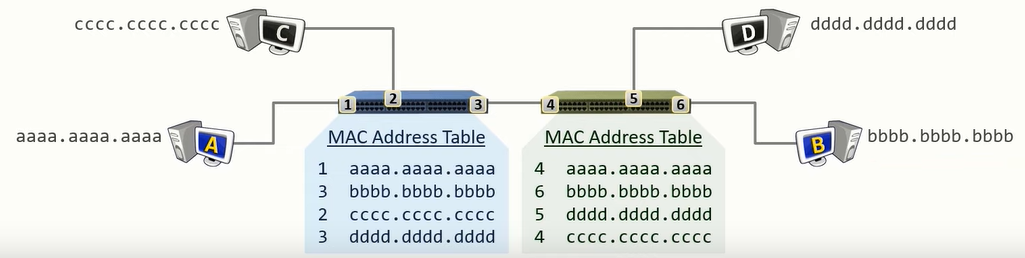
It is possible for the Switch to have multiple mappings for the same Port
This generally occurs when a Switch is connected to another Switch