Internet Protocol Security (IPSec)
A protocol suite for secure communication that provides authentication and encryption of data packets on IP networks
Used in site-to-site VPN and client-to-site VPN
Provides:
- Confidentiality (Encryption)
- Integrity (Message Digest verification)
- Authentication (Credential verification)
- Anti-replay Protection (Packet Sequence Number)
IPSec Tunnel Creation
Initiate IPSec Process
IKE Phase 1
Authenticate parties and establish secure tunnel
ISAKMP protocol is used to create tunnel
This tunnel is used to send management packets
IKE Phase 2
Negotiate security associations and establish a tunnel inside the 1st tunnel
This tunnel is used to send the data
Data Transfer
Tunnel Termination
IPSec Protocols
The protocols can be used together (VPN)
AH on its own is not commonly used as it does not encrypt the data
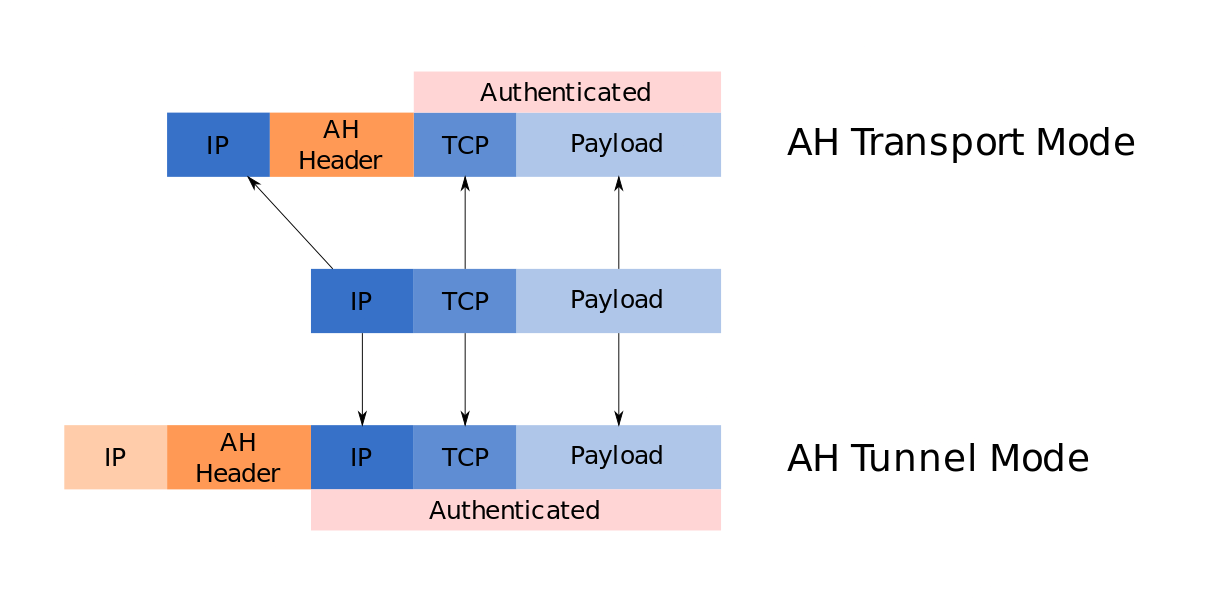
Authentication Header (AH)
AH Protocol is responsible for providing integrity and authentication
It takes the IP Header and Data Payload and Hashes them, this hash is used to create a new AH Header which is appended to the packet
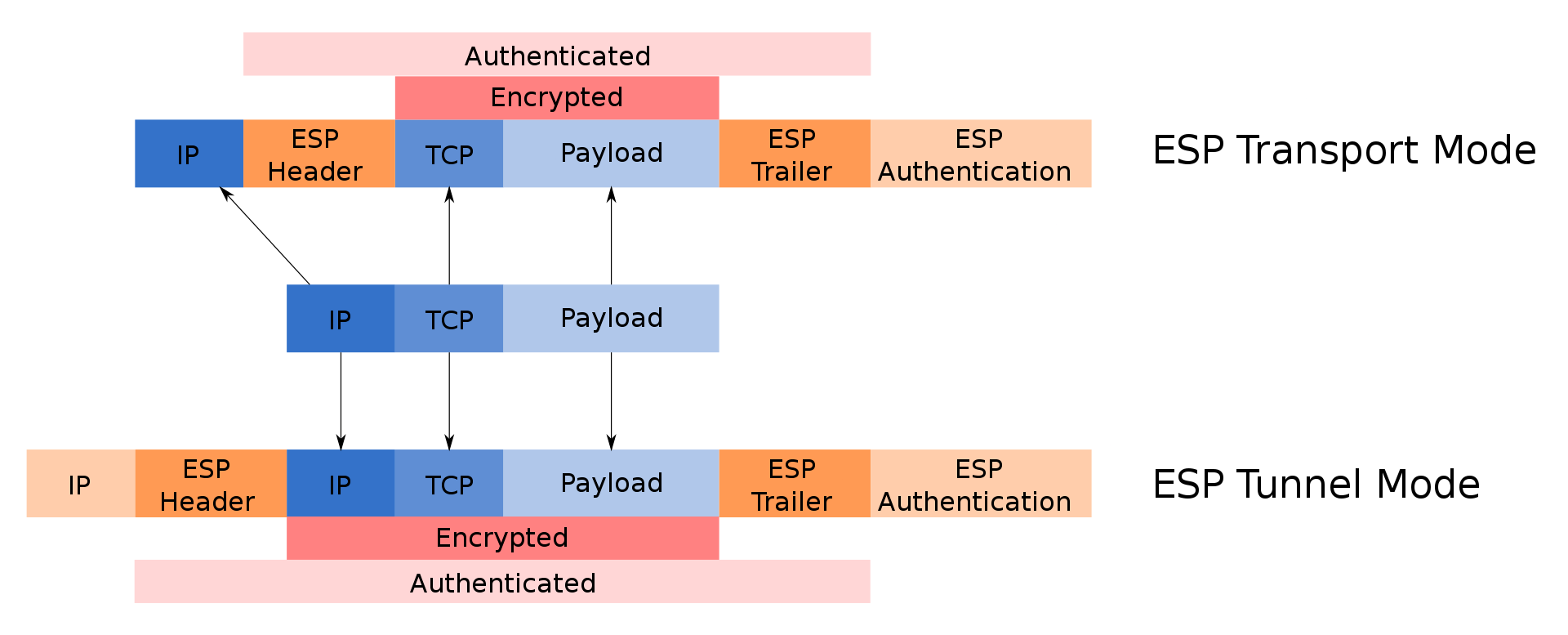
Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP)
ESP provides encryption and integrity for the data packets as they are sent over IPsec Employed for providing authentication, integrity, replay protection and data confidentiality
IPSec Operation Modes
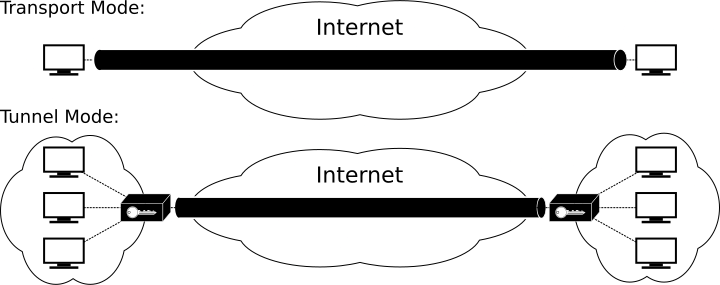
Transport Mode
Employs the original IP headers, ideal for client-to-site VPNs
Advantageous when dealing with MTU constraints
AH used for authenticate TCP and payload integrity
ESP is used to encrypt TCP header and payload and AH is for the integrity
IP header is not encrypted so the source and destination of data will be visible
Tunneling Mode
Employed for site-to-site VPNs
Adds an extra header that can increase packet size and exceed MTU