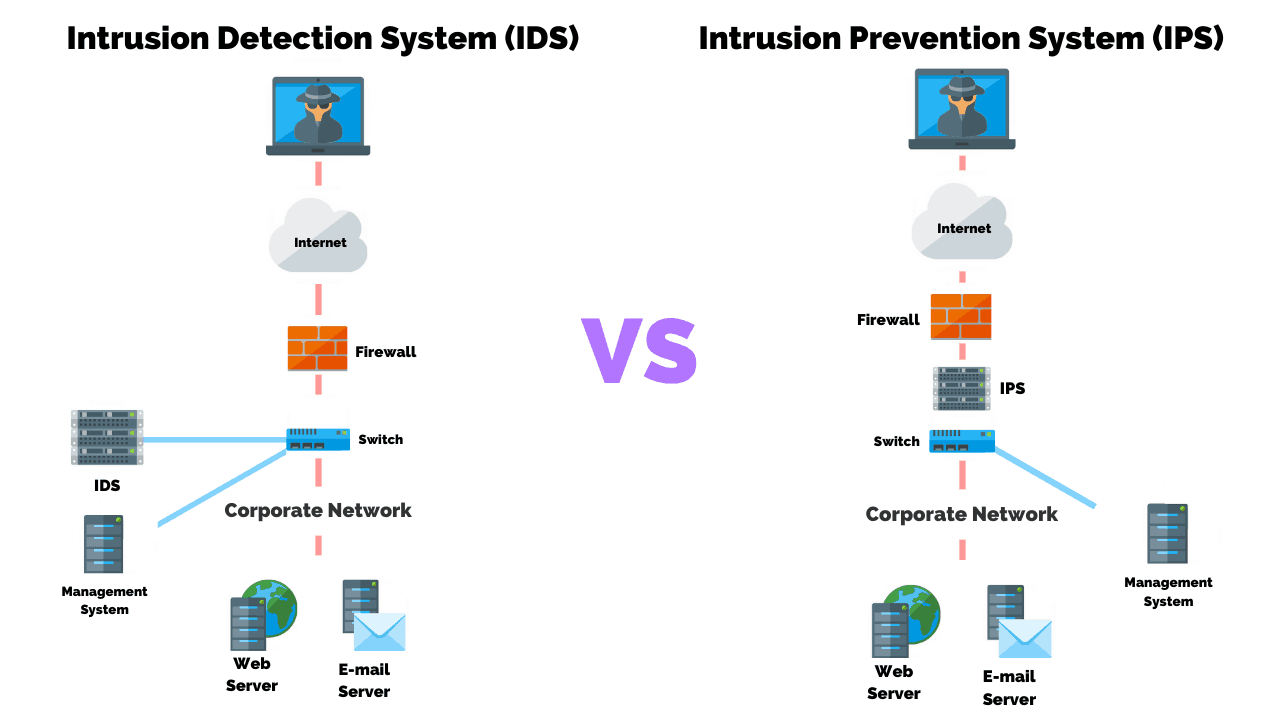
Intrusion Detection System
Detect attacks on the network and log and report the incident
Types of Alerts
True Positive: Malicious activity identified as an attack
True Negative: Legitimate activity detected so no alerts
False Positive: Legitimate activity is detected as an attack
False Negative: Malicious activity is not detected as an attack
Intrusion Prevention System
Detect attacks on network and actively try and prevent it
Makes changes to the ACL or closes services, sessions or ports
Intrusion Detection VS Prevention Systems: What’s The Difference?
IDS/IPS Types
Host-based
Called as HIDS/HIPS
Installed on servers and workstations
Detect attacks on the hosts not on the network
Will impact the hosts performance
Network-based
Called as NIDS/NIPS
Standalone device on the network
It is configured on a SPAN or mirrored port of the backbone switch
Uses sensors on the network devices to report on attacks
Cant monitor traffic of individual hosts
Wireless
Called as WIDS/WIPS
Attempts to detect DOS attacks on the wireless network
Monitoring Techniques
Signature-based Detection
Looks for a specific string of bytes to trigger an alert
Can only detect attacks based on the patterns present in its database
Pattern-matching
Specific pattern of steps
Commonly used on NIDS, WIDS
Stateful-matching
Compares against known system baseline
Commonly used on HIDS
Anomaly-based Detection
Also called Behavior-based Detection
Analyze current network traffic against established baseline traffic and alerts if outside the statistical average