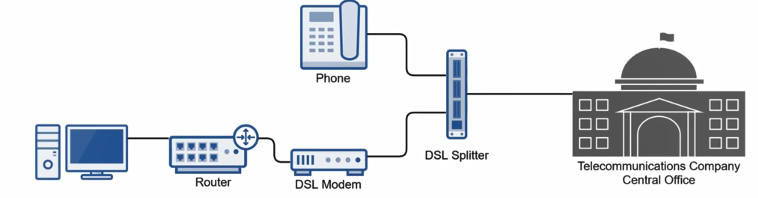
High speed internet using POTS (Sends data digitally over telephone line)
Uses a DSL modem and splitter to accomplish this task
(Limitation) DSL modem must be within 2 miles of telecommunication company
It’s an hybrid technology as the connection to the telecommunication company can be circuit switched (normal speed connection) or packet switched (high speed connection)
Symmetric DSL (SDSL)
Equal bandwidth for upstream and downstream data flows (Office Users)
1.544Mbps (US and Canada) - T1 Equivalent
2.048Mbps (Europe) - E1 Equivalent
Asymmetric DSL (ADSL)
Allocates more bandwidth for downstream than upstream (Home Users)
1.544 to 6.1Mbps Downstream and 16 to 640Kbps Upstream
Very High Bitrate DSL (VDSL)
An subset of ADSL used generally in offices
53Mbps Downstream and 2.3Mbps Upstream
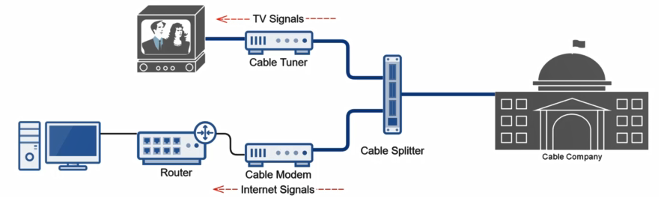
Broadband Cable
High speed Internet technology utilizing your cable service (Internet over TV cable)
Uses Data Over Cable Service Interface Specification (DOCSIS) standard to provide Internet access
Multiple signals over different frequencies at the same time in the cable (Do to different frequencies we can have multiple channels (each channel 1 frequency) and a different frequency for Internet)
It makes use of packet switched network
| DOCSIS Version | Max Download Speed | Max Upload Speed |
|---|---|---|
| 1.0 | 40Mbps | 10Mbps |
| 1.1 | 40Mbps | 10Mbps |
| 2.0 | 40Mbps | 30Mbps |
| 3.0 | 1.2Gbps | 200Mbps |
| 3.1 | 10Gbps | 1Gbps |
| 3.1 Full Duplex | 10Gbps | 10Gbps |
NOTE
3.0 onward are the newer standards that are available