Computer Virus
Code that runs on the machine without the user’s knowledge and infects the computer Viruses require user action to reproduce and spread
Boot Sector Virus
Stored in the first sector of the hard drive and loaded into memory on system boot
Very difficult to detect
Macro Virus
Code embedded into a document that is executed when opened by the user
Program Virus
Tries to find executables or application to infect with malicious code
Multipartite Virus
A virus that combines boot and program viruses
It attaches itself to the boot sector and system files before attacking other files
Encrypted Virus
Uses encryption to hide the malicious content to avoid detection
Polymorphic Virus
Advanced version of an encrypted virus that changes itself every time it is executed by altering the decryption module to avoid detection
Metamorphic Virus
Type of virus that can rewrite itself entirely before it attempts to infect a file
It is an advanced version of the polymorphic virus
Stealth Virus
A virus that uses different techniques to hide from antivirus software
Encrypted, Polymorphic and Metamorphic viruses are classified as Stealth Viruses
Armored Virus
A virus that has a layer of protection to confuse a program or person analyzing it
Virus Hoax
It is not a type of virus
It is an attempt (Social Engineering) to get the user to install a virus on their system
Worm
Malicious software that is like a virus but can replicate itself without any user interaction
Worms can disrupt normal network traffic and computing activities
Exploits security vulnerabilities to spread and replicate
e.g. Nimda, Conficker
Trojan
Malicious software that is disguised as a piece of harmless software or desirable software
Remote Access Trojan (RAT)
Providers the attacker with remote control of a victim’s computer and is the most commonly used type of trojan
Ransomware
Uses a vulnerability in your software to gain access and then encrypts all the files
Form of Blackmail and Extortion
Backup Data, Update Software, Security Awareness Training, MFA
e.g. Dusseldorf Hospital (Germany), Colonial Pipeline
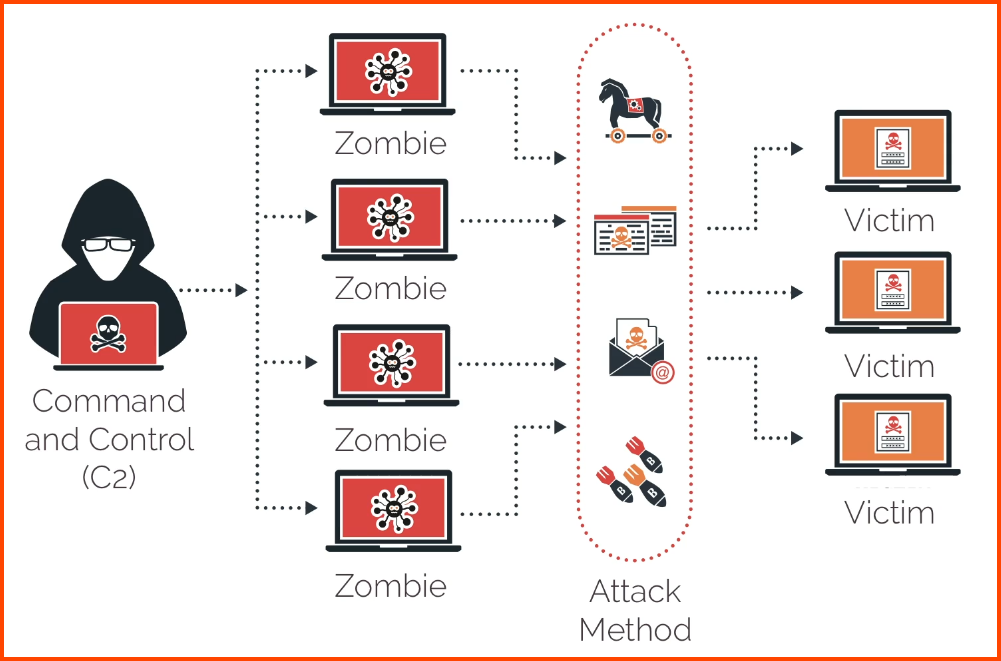
Botnets & Zombies
Botnet
A collection of compromised devices under the control of a master node
They are great for anything that is processing intensive
Used for sending out phishing emails, malware and conducing DDoS attacks
Zombie
A compromised device that is part of the botnet
Rootkit
Software designed to gain administrative level control on the system without detection
Rootkits are loaded before booting the OS and are difficult to detect and remove
External systems scans are required to detect rootkit
Ring 0: Kernel Mode
Ring 1: Administrator Mode
Ring 3: User Mode
DDL Injection
Technique used to load malicious code into a running process by taking advantage of DDLs that are loaded at runtime
DDLs are modular code and data that can be used by multiple programs
The attack is achieved by using a shim. A shim is an interface that is placed between two components to intercept calls and redirect them
Backdoor
Used to bypass the normal security and authentication functionality of a application
Remote Access Trojan (RAT) is an example of Backdoor
Logic Bomb
Malicious code that has been inserted into the program that is only executed when a certain condition is met
Keylogger
Software or hardware that records every single keystroke that is made by a device
Identity Theft, Financial Fraud, Corporate Espionage
Update Software, Good Antivirus, Phishing Awareness Training, MFA, Encrypt Keystrokes, Physical Checks
Spyware & Bloatware
Malware that secretly gathers information about the user without their consent
Could sometimes captures users keystrokes (keylogger) and take screenshots that are then sent to the attacker
Bloatware: Any software that comes pre-installed on a new system
Adware: Displays ads based on the information its spying from you
Grayware: Software that isn’t malicious but tends to behave improperly