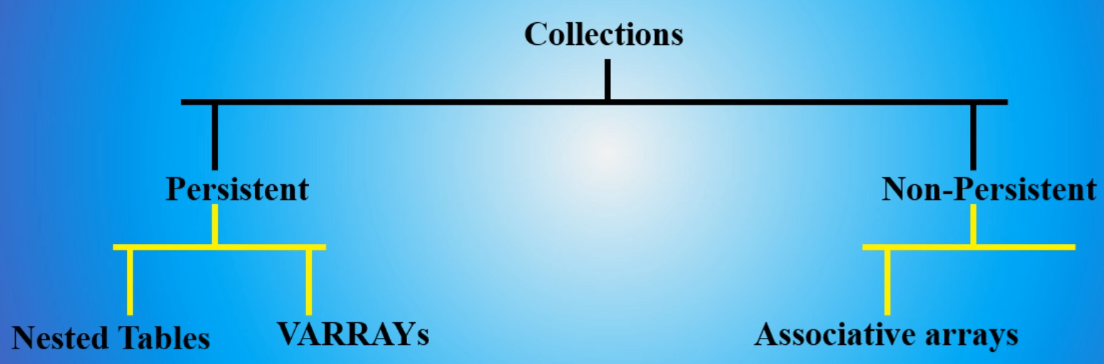
Collections in SQL are one dimensional and are similar to arrays
VARRAYs have an upper bound on the size
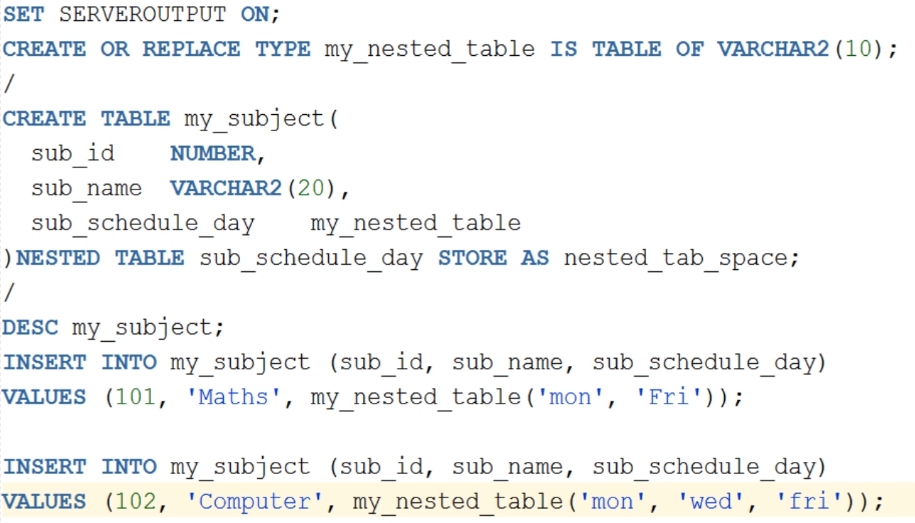
Nested Table
Similar to array. Index starts from 1
COUNT can be used to find the size of the nested table
How To Create Nested Table As Database Object In Oracle | RebellionRider
SET SERVEROUTPUT ON;
DECLARE
TYPE nested_table IS TABLE OF NUMBER;
v_array nested_table := nested_table(0,1,2,3,4);
BEGIN
FOR i in 1 .. v_array.COUNT
LOOP
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE(i || ' => ' || v_array(i));
END LOOP;
END;
/

VARRAYs
The LIMIT keyword is used to access the upper limit of the VARRAY
The EXTEND keyword is used to initialize the VARRAY. When used outside the loop we use EXTEND(n) when using inside the loop for dynamic allocation we just use EXTEND
The values can be directly specified in the initialization step as well
Introduction To PL/SQL VARRAYs In Oracle Database | RebellionRider
How To Create VARRAYs As Database Object In Oracle Database | RebellionRider
SET SERVEROUTPUT ON;
DECLARE
TYPE varray_type IS VARRAY(10) OF NUMBER;
new_varray varray_type := varray_type();
BEGIN
new_varray.EXTEND(10);
FOR i in 1 .. new_varray.LIMIT
LOOP
--new_varray.EXTEND;
new_varray(i) := i * 10;
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE(new_varray(i));
END LOOP;
END;
/Associative Array
Similar to dictionary (key, value) pair from other programming languages
SET SERVEROUTPUT ON;
DECLARE
TYPE ass_array IS TABLE OF NUMBER
INDEX BY VARCHAR2(20);
array ass_array;
counter VARCHAR2(20);
BEGIN
array('Book 1') := 1234;
array('Book 2') := 5678;
array('Book 3') := 91011;
counter := array.FIRST;
WHILE counter IS NOT NULL
LOOP
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('Key : ' || counter || ' Value : ' || array(counter));
counter := array.NEXT(counter);
END LOOP;
END;
/Functions
COUNT: Can be used in For loop as upper bound. Returns the number of elements that are present in the collection (Used with Nested Table)
EXISTS(n) : Used to check if an value is present at an index
FIRST, LAST: Returns the first and last element of an collection. Returns NULL if collection does not have value. Error if Index does not exist
LIMIT: Can be used in for loop as upper bound. Returns the size of the VARRAY
PRIOR(n), NEXT(n): Returns the previous and next index
Procedures
DELETE, DELETE(n), DELETE(start, end): Deletes an value at an index from the collection
EXTEND, EXTEND(n), EXTEND(n, v): It is used to assign memory. Attach a single NULL value. Append NULL n times. Append n times the value at index v. Cannot be used with associative arrays
TRIM, TRIM(n): Remove 1 element from end. Remove n elements from end