Built-in types - C# reference | Microsoft Docs
Constants must be initialized during declaration
Variable names cannot start with a number
Reserved keywords shouldn’t be used as variables names. If they have to used it needs to be prefixed with the @ sign
Strings in C# are enclosed in double quotes (”…“)
Characters in C# are enclosed in single quotes (’…‘)
When we compile C# code each datatype is converted to its equivalent .NET datatype
All datatypes in C# are derived or extended from the System.Object
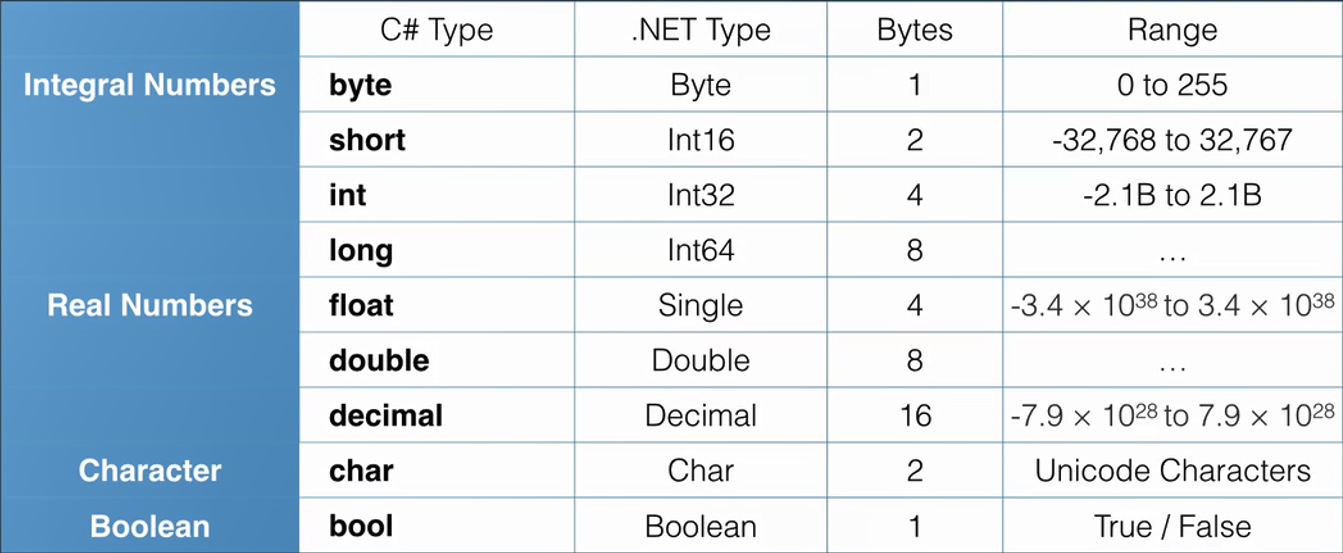
The default real number type is “double”. The other types need to be declared explicitly
float num1 = 2.1f;
decimal num2 = 2.21m;var datatype tells C# to automatically infer datatype
It can only be used if the variable is initialized and declared on the same line
Declare variables in C# using the .NET equivalent types is also possible
The type of an object can be checked by using the FullName property of the GetType() class
string name1 = "Irene";
String name2 = "Wendy";
Console.WriteLine("{0}, {1}", name1, name2);
int num1 = 12;
Int32 num2 = 13;
Console.WriteLine("{0}, {1}", num1, num2);
Console.WriteLine(name1.GetType().FullName);