Operators
All the other arithmetic operators (leaving %) allows integer and floating point operands
When a int and float is involved the result (exception % and /) is always a float
With / if both the operand is integer then the result is also a integer
With % floats cannot be used
C89
Division with a negative operand, the result will be rounded up or down
Remainders results depends on the implementation (a % b = a - (a/b) * b)
C99
Division with a negative operand is always rounded towards 0
Remainder uses the same sign as i (i % j) for the result
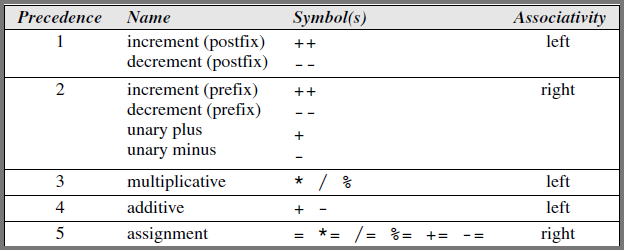
Associativity
When we have multiple operators with the same precedence we use associativity
Unary Operators are Right Associative (Calculated from right-to-left)
e.g. - + i = -(+i)
Assignment
v = e (Simple Assignment)
If e and v do not have the same type e is converted to the type of v at assignment
= Operator
In C assignment = is considered a operator (not a statement)
Because of this we can have chain assignments
It is a operator that has a side effect (Causes the value of v to change)
Assignment operator is right associative
L-value (Locator Value)
L-values represents an object stored in computer memory
The assignment operator requires an L-value as its right operand
Variables and Compound Literals are a type of L-value
Understanding lvalues and rvalues in C and C++ - Eli Bendersky’s website
Compound Assignment
Old value of variable is used to compute the new value of variable
e.g. i = i + 2
Compound assignments allow shorthand notation
e.g. i += 2
There are nine of them in total including -=, *=, /=, %=
Increment & Decrement
Increment and Decrement shorthand (++ & --)
Similar to = they have side effects
++i: Increment value immediately
i++: Use old value increment later
Side Effects
The output of these expressions are undefined in C:
c = (b = a + 2) - (a = 1);
j = i * i++;
Avoid chaining operators with side effect
In C any expression can be used as a statement by simply ending it with a semicolon
e.g. i * j - 1;
These statements have no effect unless the operation has a side-effect
e.g. ++i;
The side-effects of a operation are guaranteed to be computed by the next sequence point (sequencing) in the program
Sequence point - Wikipedia