Data Types
The data types is an attribute of data that tells the compiler how the developer intends to use the data. This also defines the type of operations that can be performed on it.
The data type defines the capabilities and the constraints of the data
>>> class War:
... pass
>>> type(War)
<class 'type'>
>>> type
<class 'type'>
>>> type(type)
<class 'type'>
>>> type(War) == type(type)
TrueClasses
Classes in Python are Mutable
We can use the dot notation and and new attributes and methods to it
We cannot do this on type as its implemented in C (it is an extension type) and is immutable
A class is a Callable (like a function) that returns an instance
Class is a thing that allows to construct instances
The __class__ property of the instance holds an reference to Class that created it
class Car():
def __init__(self, color: str) -> None:
self.color = color
def drive(self) -> str:
print("We are driving the Car")
car1 = Car('red')
print(car1.__class__.__dict__)
>>> mappingproxy({'__module__': '__main__', '__init__': <function __main__.Car.__init__(self, color: str) -> None>, 'drive': <function __main__.Car.drive(self) -> str>, '__dict__': <attribute '__dict__' of 'Car' objects>, '__weakref__': <attribute '__weakref__' of 'Car' objects>, '__doc__': None})
print(car1.__class__.__bases__)
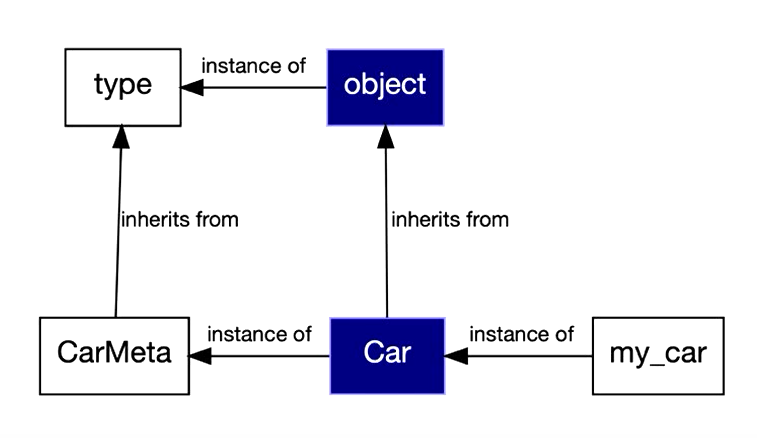
>>> <class 'object'>The __dict__ of the class returns an mapping proxy (a read-only dictionary) which contains the attributes of the class
The __bases__ attribute of a class points to all its parent classes. In Python all classes inherent from the object class
_new_ Method
The __new__ method is responsible for creating the instance of a class. Before the __new__ is called the class is not instantiated
This method is called before the __init__ method
It is a class method, if we don’t specify this method it is inherited from the object class
Inheritance
An attribute lookup on an object looks as follows:
Instance → Class Definition → Super classes → Raise Attribute Error
The __getattr__ can be used an an fallback to perform some operation just before Attribute Error is raised
The __getattribute__ method is another method that is called even before the attribute is looked up on the Instance
The entire flow of the lookup looks as follows:
__getattribute__ → Instance → Class Definition → Super classes → __getattr__ → Raise Attribute Error
If the __getattribute__ method where to raise a Attribute Error then all the other lookups would be bypassed and directly __getattr__ would be called
MRO is used to decide the order in which the attributes and methods should be called when classes inherent and overwrite features
A descriptor is an object attribute with “binding behavior”, one whose attribute access has been overridden by methods in the descriptor protocol.
Property in Python are implemented using the descriptor protocol
When a __set__ method is defined for an attribute then the flow of the lookup changes:
__getattribute__ → Data Descriptor in class dict → Instance → Class Definition → Super classes → __getattr__ → Raise Attribute Error
Methods
In Python methods are wrappers around the function that is declared in the class
A method encapsulated the self parameter with the function (hence why we don’t have to pass self when we call the method)
print(Car.drive)
>> <function Car.drive at 0x0000020AFC2303A0>
print(car1.drive)
>> <bound method Car.drive of <__main__.Car object at 0x0000020AFCBDD640>>
print(Car.drive.__get__(car1, Car))
>> <bound method Car.drive of <__main__.Car object at 0x0000020AFCBDD640>>Metaclasses
We can create a new Class using type() in its overloaded form
The Class keyword also behind the scenes calls the type() to create the class
Metaclasses are custom classes that allow the user to modify the default behavior of class that is created using type()
def init_func(self, color: str) -> None:
self.color = color
def drive(self) -> None:
print(f"We are driving a {self.color} Car")
MagicCar = type('MagicCar', (object,),
{'__init__': init_func, 'drive': drive}
)
new_car = MagicCar('red')
print(new_car.drive())A metaclass is a Callable that returns a class
Even before __new__ is called there is an method called __prepare__ which is called which returns a dictionary that stored everything that is inside a class
Adding a method to an existing object instance - Stack Overflow