Rebase is used to move an branch from its current location and append it on top of another branch
Rebase causes the order in which the events have occurred to change
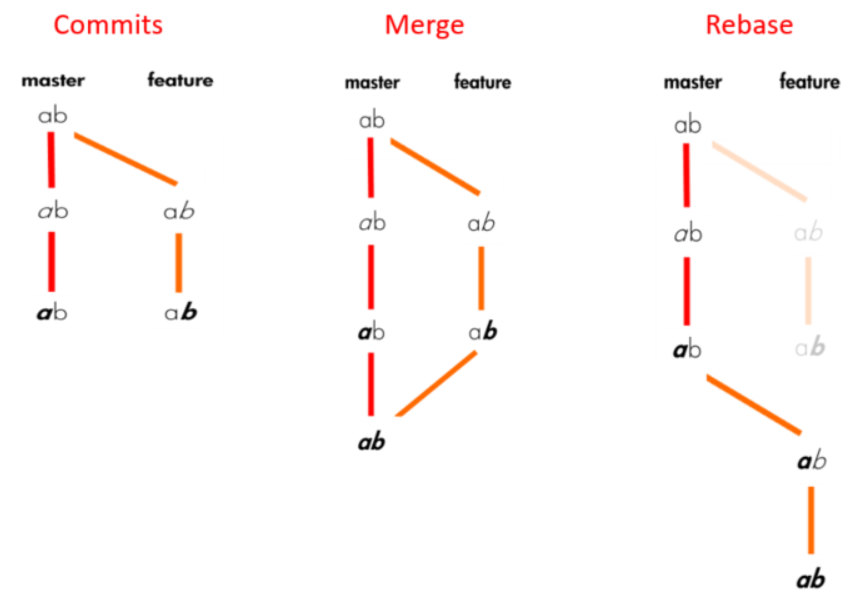
# Rebase current branch on top of base branch
git rebase <base-branch>
# Append branch to rebase on top of base branch
git rebase <base-branch> <branch-to-rebase>
# Rebase in interactive mode
git rebase -i <base-branch>While in Interactive mode we have choice on what needs to be done to each of the commit on that branch. The commonly used options are pick and squash
Squash will merge those commits into an single commit
Interactive mode is especially useful when rebasing each commit in the rebase can cause conflict by squashing them into one commit we can make rebasing simpler
# Continue rebase after fixing merge conflict
git rebase --continue
# Can be used to ignore an conflict while rebasing
git rebase --skip
# Used to abort the rebase operation
git rebase --abortImportant
- After performing an rebase to push changes to upstream we will have to use the
-fflag- The local repo and the upstream do not match at this point hence upstream has to be overwritten with local copy
GIT Rebase vs GIT Merge for Novices | by Justin Tulk | Medium
An introduction to Git merge and rebase: what they are, and how to use them
When to use ‘Git Rebase’ explained | by Harish Yadav | Medium