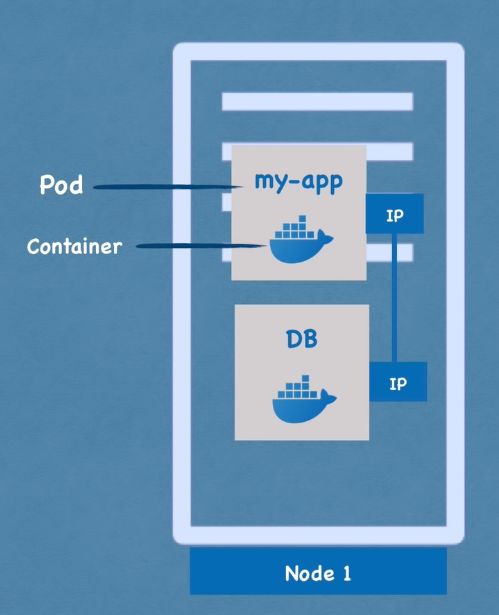
Pods
The smallest unit of K8s. It is an abstraction layer over containers
A pod is meant to mostly run a single container
But multiple containers can be run in a single Pod (used if the main container has a helper service that is tightly coupled with the main container)
Each Pod in K8s is assigned its own Virtual Private IP Address
If a container crashes and it’s restarted it will be assigned a new IP Address
Service
It is a Permanent Private IP Address that can be assigned to each Pod
The lifecycle of Pod and Container are not connected (If Pod restarts the IP will remain the same)
Types of Services: Kubernetes Services
Config Map & Secrets
Config Map is used to store the external configuration of our applications (Environment Variables)
The config has to be connected/ applied to a Pod
Credentials and Secrets should not be stored in Config Map (Use Secrets instead)
The value of data stored in Secret has to be base64 encoded
Important
- Storing the data in secret component does not automatically make it secure
- There are build-in features like encryption (default not enabled) that need to be used
The data from Config Map and Secrets can be accessed in Pod like an Environment Variable or Configuration File
Controller
Used for creating/ updating pods and other objects (Rules for managing K8s objects)
Multiple Types: Deployment, ReplicaSet, DaemonSet, StatefulSet, Cron, CronJob
Deployment
It is a type of Controller. Blueprint of actions to be performed on the Pods
It is an abstraction over the Pods which makes it more convenient to talk with the Pods
Provides the ability to create replicas of the Pods
DBs cannot be replicated using Deployments (As DBs are stateful)
StatefulSet
It is used when the state of the Pod needs to be maintained across multiple replicas of the Pod
Along with replication provides additional mechanisms to maintain data consistency