Large Scale System - Data cannot be stored on single server
So Data needs to be Distributed across multiple nodes
For predictable performance distributed data needs to be evenly on all servers
serverIndex = Hash(Key) % N
N = No. of ServersNormal Hashing
The key of Object is hashed using hashing function which produces an numeric values which falls in a defined range (hash space). A good hash function evenly distribute the object keys across the hash space
The modulo operation between this range and the no. of servers is performed to find the server on which the object will reside
Drawback
This approach works well when the no. of clusters in the system is fixed
When new servers are added to the cluster or a server in the cluster goes down there will be a storm of data redistribution and data misses
Will the hash values do not need to be recomputed the no. of servers will be different and so is the mapping of the server to which the data belongs
In systems where servers are continuously added and removed this type of design is untenable
Consistent Hashing
Instead of just hashing the objects the server names are also hashed
They are both hashed using the same hashing function and will map to the same hash space
The start and end of the hash space are connected to create a hash ring
The server names (IP Addresses) are hashed and added to the ring
Similarly, the objects are hashed and added onto the ring (the modulo operation is not performed)
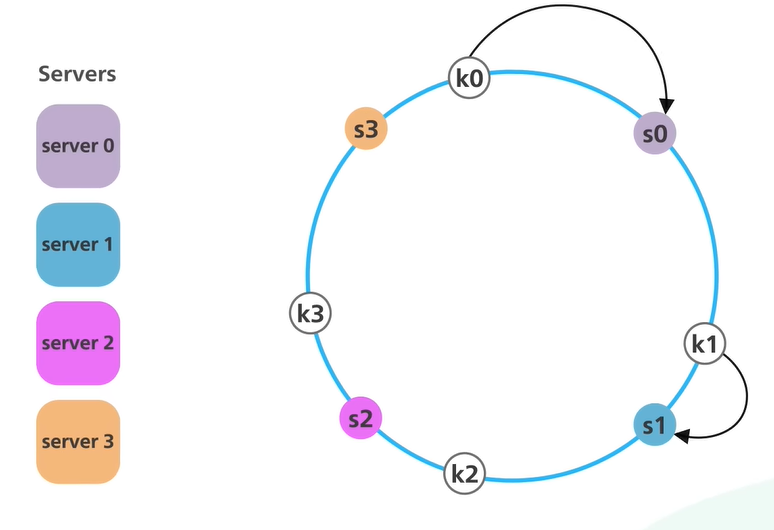
To find the node to which the data will belong we just need to look to the right (clockwise direction) and find the first node
Because of this approach even when a new server is added to the system only a fraction of the keys need to be redistributed
Drawbacks
When the distribution of the servers and objects is not even then a large amount of the data could belong to a single server
This gets even worse when constantly servers are added and removed from the cluster
Solution
Virtual nodes are used instead of physical nodes
Virtual nodes can appear at different locations on the ring
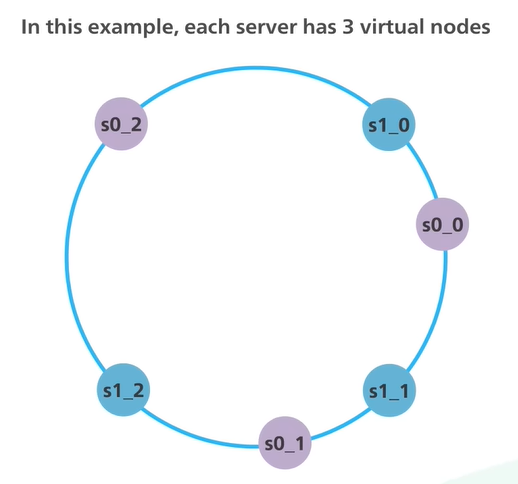
With virtual nodes, each server handles multiple segments on the ring
In real-world applications, the number of virtual nodes is much greater than three and this makes the distribution of data more even
Additional space is required to store metadata related to the virtual servers